reading-notes
Linked List
- A Linked List is a sequence of Nodes that are connected/linked to each other. The most defining feature of a Linked List is that each Node references the next Node in the link.
- There are two types of Linked List - Singly and Doubly. We will be implementing a Singly Linked List in this implementation.

- A linked list is a sequence of data elements, which are connected together via links. Each data element contains a connection to another data element in form of a pointer. Python does not have linked lists in its standard library. We implement the concept of linked lists using the concept of nodes. Each element of a linked list is called a node, and every node has two different fields.
- Data contains the value to be stored in the node.
- Next contains a reference to the next node on the list.
Why Linked List?
- Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have the following limitations.
- The size of the arrays is fixed: So we must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to the upper limit irrespective of the usage.
- Inserting a new element in an array of elements is expensive because the room has to be created for the new elements and to create room existing elements have to be shifted.
- A linked list is created by using the node class. We create a Node object and create another class to use this ode object. We pass the appropriate values thorugh the node object to point to the next data elements. The below program creates the linked list with three data elements.
Linear data structures
- If we really want to understand the basics of linked lists, it’s important that we talk about what type of data structure they are. One characteristic of linked lists is that they are linear data structures, which means that there is a sequence and an order to how they are constructed and traversed.
Memory management
The biggest differentiator between arrays and linked lists is the way that they use memory in our machines. Those of us who work with dynamically typed languages like Ruby, JavaScript, or Python don’t have to think about how much memory an array uses when we write our code on a day to day basis because there are several layers of abstraction that end up with us not having to worry about memory allocation at all.
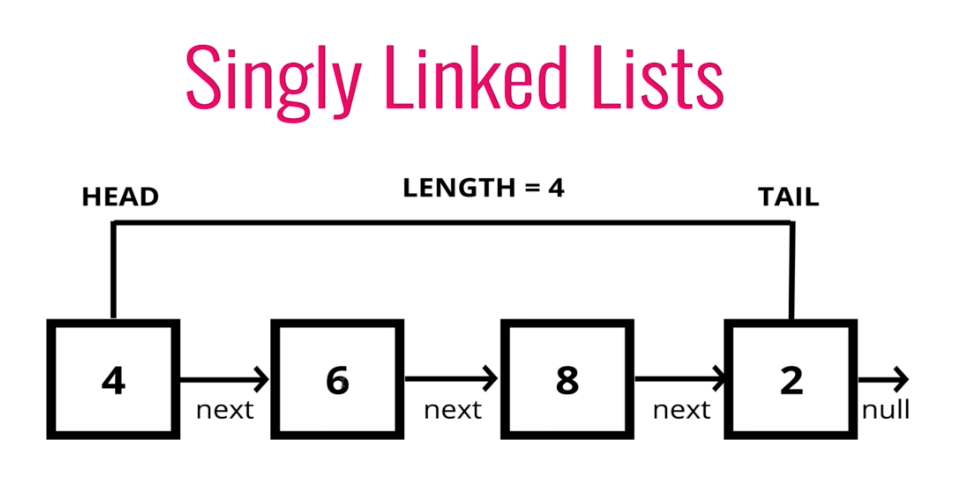
Parts of a linked list
A linked list can be small or huge, but no matter the size, the parts that make it up are actually fairly simple. A linked list is made up of a series of nodes, which are the elements of the list. The starting point of the list is a reference to the first node, which is referred to as the head. Nearly all linked lists must have a head, because this is effectively the only entry point to the list and all of its elements, and without it, you wouldn’t know where to start! The end of the list isn’t a node, but rather a node that points to null, or an empty value.